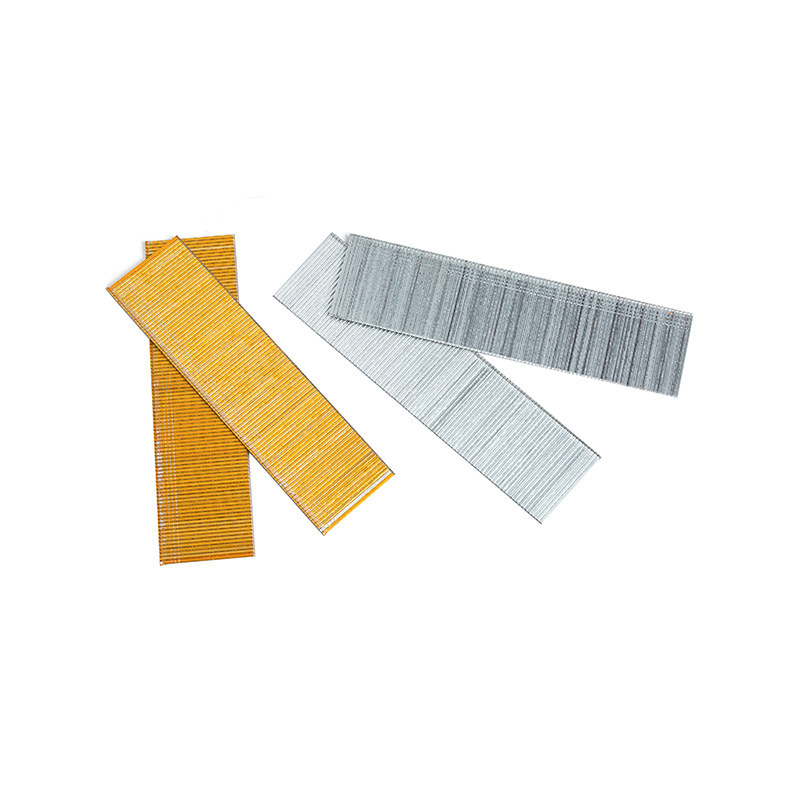
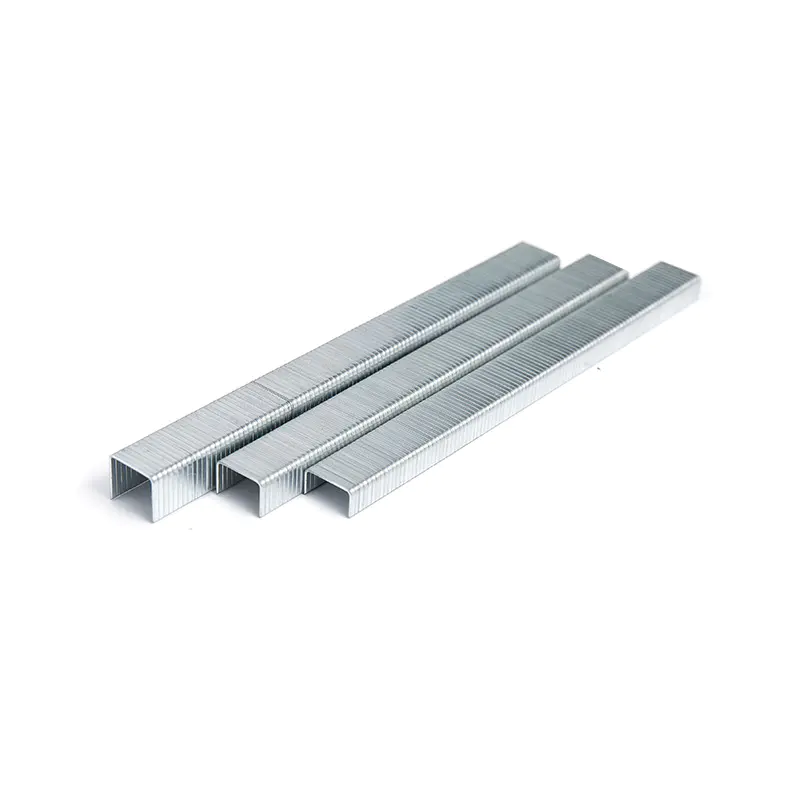
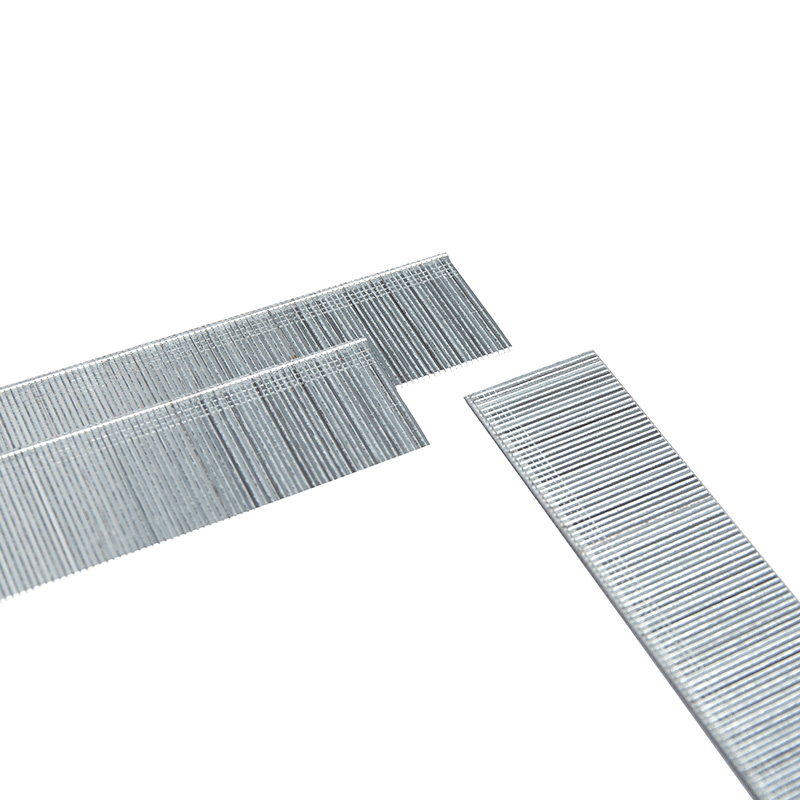
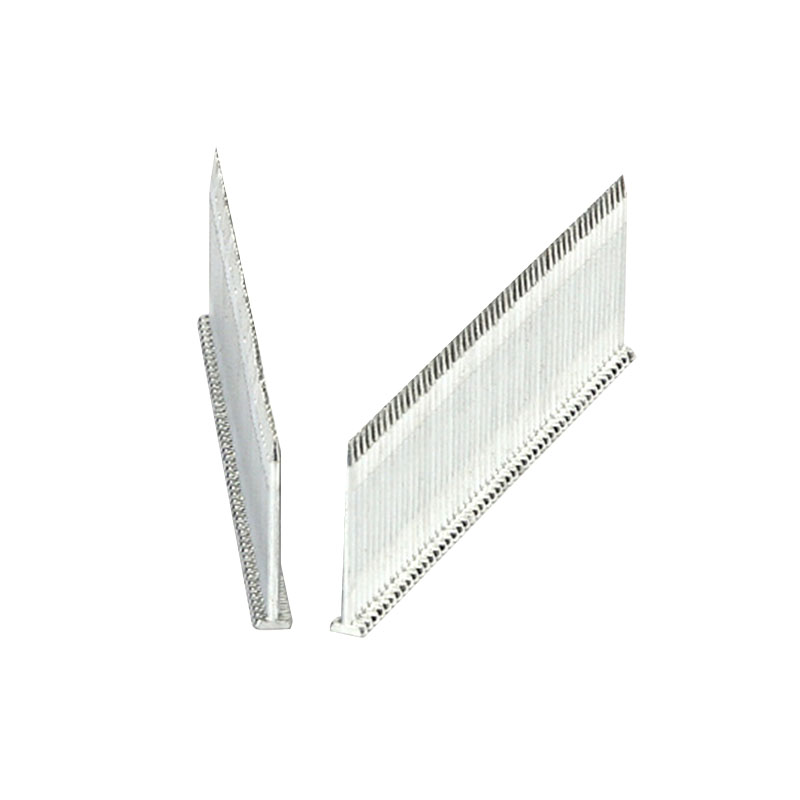
In the high-precision world of industrial fastening, the synergy between a pneumatic tool and its consumable is the thin line between operational efficiency and costly downtime. For procurement officers and engineers, understanding the technical nuances of Thin Line Staples is essential. While these fasteners are celebrated for their ability to provide a discreet yet powerful hold, their compatibility with various pneumatic systems is governed by strict mechanical tolerances and material science.
As a leading authority in the fastener industry, Zhejiang Tianying Hardware Co., Ltd. has leveraged over two decades of manufacturing heritage to refine the production of industrial grade thin wire staples. Established in 2017—building upon a 21-year legacy from the original Hangzhou Tianying Gunners factory—our facility in Anji serves the Yangtze River Delta economic zone with advanced research, design, and production capabilities. We understand that for a professional, a staple is not just a piece of bent wire; it is a critical component of structural integrity.
The Engineering Behind Thin Line Staples Compatibility
Compatibility in pneumatic systems is primarily dictated by the "magazine geometry" and the "driving blade width." Thin Line Staples, typically categorized by their high gauge number (indicating a thinner wire), require a driver blade that matches their crown width and wire thickness precisely. If the staple is too thin for the tool’s guide track, "buckling" or "double-feeding" occurs.
According to the 2024 Global Industrial Fastener Market Analysis by the International Fasteners Institute, there has been a significant shift toward corrosion resistant thin line fasteners in the construction and upholstery sectors. This trend is driven by increased environmental regulations requiring longer product lifespans and higher resistance to oxidation in humid climates.
Source: International Fasteners Institute - 2024 Market Trends Report
Technical Comparison: Standard vs. Thin Line Systems
When evaluating the mechanical fit, it is important to distinguish between the physical footprint of standard fasteners and Thin Line Staples.
| Feature | Standard Staples | Thin Line Staples |
| Wire Gauge | Typically 16 to 18 Gauge | Typically 20 to 23 Gauge |
| Penetration Resistance | High; requires more PSI | Low; preserves delicate substrates |
| Visible Footprint | Noticeable crown width | Minimal visibility for aesthetic finishes |
Critical Factors in Pneumatic Tool Integration
To ensure that Thin Line Staples function correctly across different pneumatic platforms, engineers must look at the galvanized thin line staple specs. The galvanization layer adds a fractional thickness to the base wire. In a precision-engineered tool, a variance of even 0.01mm can lead to internal friction.
- Magazine Clearance: The internal width of the stapler's magazine must accommodate the outer crown width without excessive lateral play.
- Driving Force Adjustment: Pneumatic tools used for Thin Line Staples often require lower air pressure (PSI) to prevent the thin wire from slicing through the material rather than securing it.
- Collation Integrity: The adhesive used to hold the staples together must be strong enough to resist vibration but brittle enough to shear cleanly when struck by the driver blade.
Material Performance Comparison
The choice of material directly impacts the tensile strength thin line staples exhibit during high-speed firing cycles.
| Material Type | Impact on Tool Wear | Structural Integrity |
| Basic Carbon Steel | Moderate; requires frequent lubrication | Standard; prone to bending in hardwoods |
| High-Tensile Alloy | Low; clean shearing action | Superior; resists deformation under pressure |
The Evolution of Fastening Standards in 2025
Looking toward 2025, the industry is seeing a move toward "Smart Fastening" where tool tolerances are tighter than ever. Data from the European Tool Committee (CEO) indicates that the wholesale thin line staples market is increasingly demanding tighter tolerances on wire diameter consistency to satisfy the requirements of automated robotic fastening lines.
Source: European Tool Committee - Annual Technical Bulletin 2025
Zhejiang Tianying Hardware Co., Ltd. adheres to a strict policy of "quality for survival, development, and benefit." Our precision engineered thin wire staples are designed to meet these evolving global standards, ensuring that whether you are using a manual decorative gun or a high-cycle industrial pneumatic stapler, the feed remains consistent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I use 22-gauge Thin Line Staples in an 18-gauge stapler?
No. The driver blade of an 18-gauge tool is too wide and will likely cause the 22-gauge staple to jam or buckle within the guide track.
2. How does tensile strength affect pneumatic tool performance?
Higher tensile strength thin line staples ensure that the staple legs drive straight into dense materials like MDF or hardwood without deviating, which protects the tool's nozzle from internal damage.
3. Are galvanized staples necessary for interior upholstery?
While corrosion resistant thin line fasteners are essential for outdoor use, they are also recommended for interior upholstery to prevent "bleeding" or rust spots if the fabric is ever cleaned with liquid solutions.
4. What is the advantage of sourcing from a specialized manufacturer like Zhejiang Tianying Hardware?
With a history dating back 21 years to the original Hangzhou Tianying Gunners factory, we offer deep technical expertise and self-management import/export rights, ensuring rigorous quality control over every batch of industrial grade thin wire staples.
5. Do different pneumatic brands require different glue types on the staple strips?
While most tools are compatible with standard chemical collation, precision engineered thin wire staples use optimized bonding agents that ensure the strip remains intact during transport but separates effortlessly during the firing sequence, reducing "gumming" in the tool head.